Project goal: (1) To assess the role of Gab2 in CSF-1 signaling; (2) To identify the function of Gab proteins in neurogenesis
CSF-1 signaling in monocyte, macrophage development in the bone marrow: role of Gab2
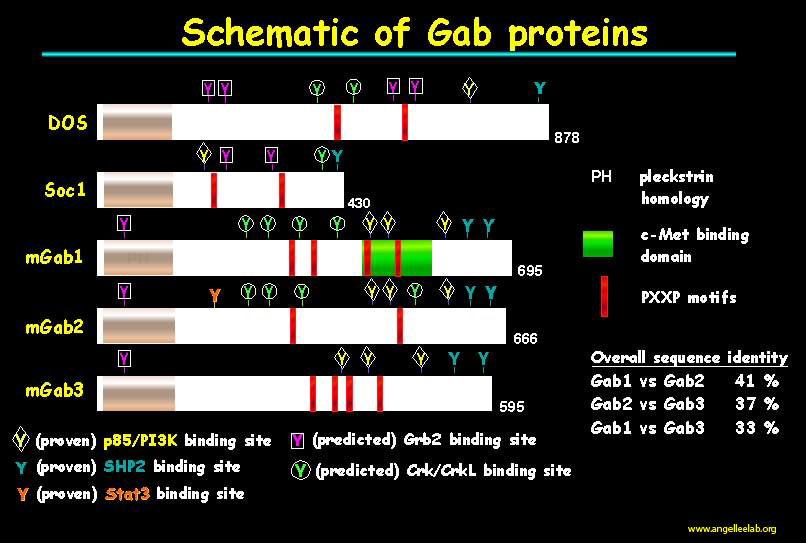
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) can couple to PI3K by recruiting molecules with PI3K binding motifs (pYXXM, X = any residue), such as the newly-discovered docking/scaffolding protein, Gab2. Recent data show that Gab2 may play a critical role in mediating cellular transformation. Data supporting a role for Gab2 in CSF-1-dependent signaling is our observation that CSF-1 stimulates Gab2 tyrosyl phosphorylation and association with p85/PI3K in 32D cells expressing either WT or DKI CSF-1R (receptor lacking kinase insert). Data implicating Src kinases as upstream regulators of Gab2 is our finding that chemical inhibition of Src activity not only altered CSF-1-induced Gab2 tyrosyl phosphorylation in WT cells but eliminated altogether CSF-1-mediated Gab2 tyrosyl phosphorylation and p85 association in DKI cells (Lee and States, Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:6779-98, 2000).
Using Gab2 knockout mice, we have shown that Gab2 is a novel regulator of monocyte, macrophage development in the bone marrow. Using a single cell flow cytometry assay that couples cell surface immunophenotyping with intracellular signaling, we demonstrated that the PI3K-Akt-S6 and Erk pathways function synergistically downstream of Gab2 to promote commitment of early myeloid progenitors to the monocyte, macrophage lineage (Lee et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 31:4563-81, 2011). You can read about it here.
These results have extended our understanding of how RTKs utilize docking proteins to diversify signal output.
Gab2 in Neurogenesis
Several years ago, we discovered that Gab2 has a role in neurogenesis. Read all about it here.
This is very interesting because there is now an established role for Gab2 as a risk factor in Alzheimer's disease.
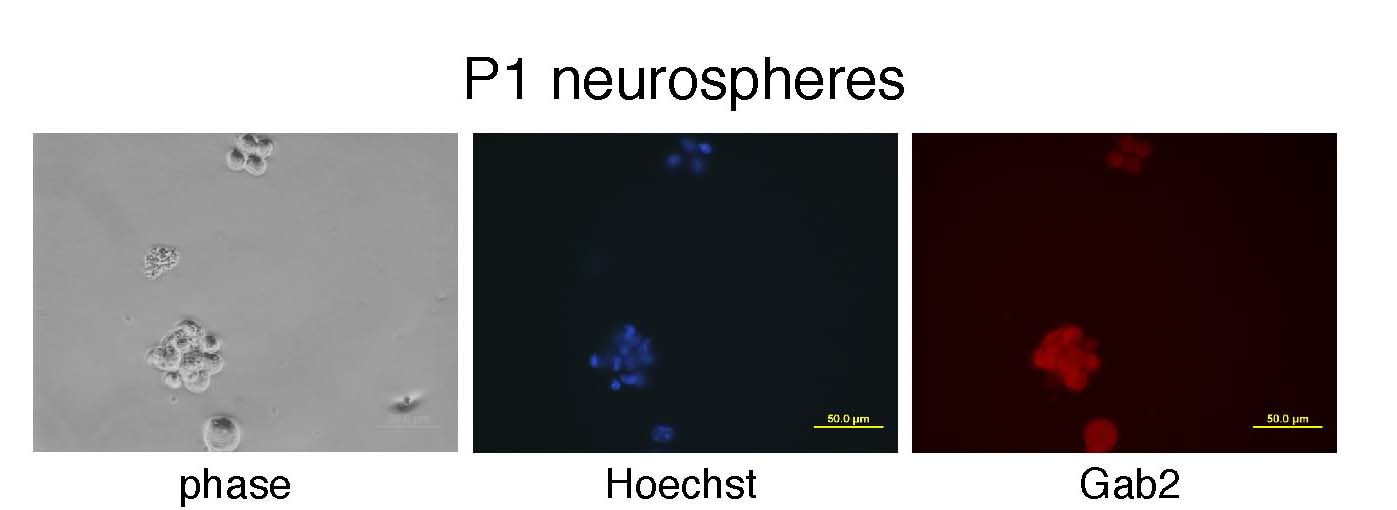
Neural stem cells isolated from the subventricular zone (SVZ) of postnatal mice were grown in culture as floating neurospheres. Immunostaining demonstrates the presence of Gab2.
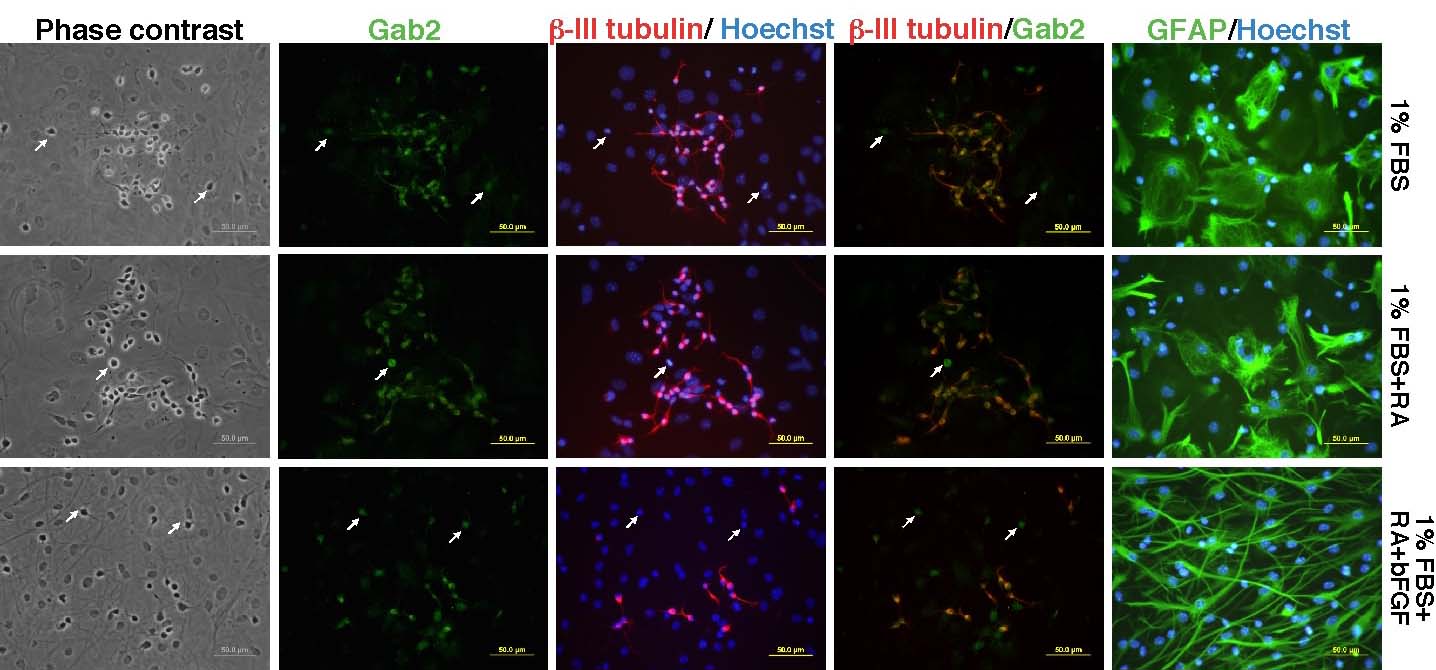
P1 neurospheres were differentiated in the conditions indicated. 7 days later, cells were stained for neurons (Tuj1), Gab2 or astrocytes (GFAP). Hoechest staining identifies all nuclei in culture. Gab2 is present in neurons but appears to be absent from astrocytes.
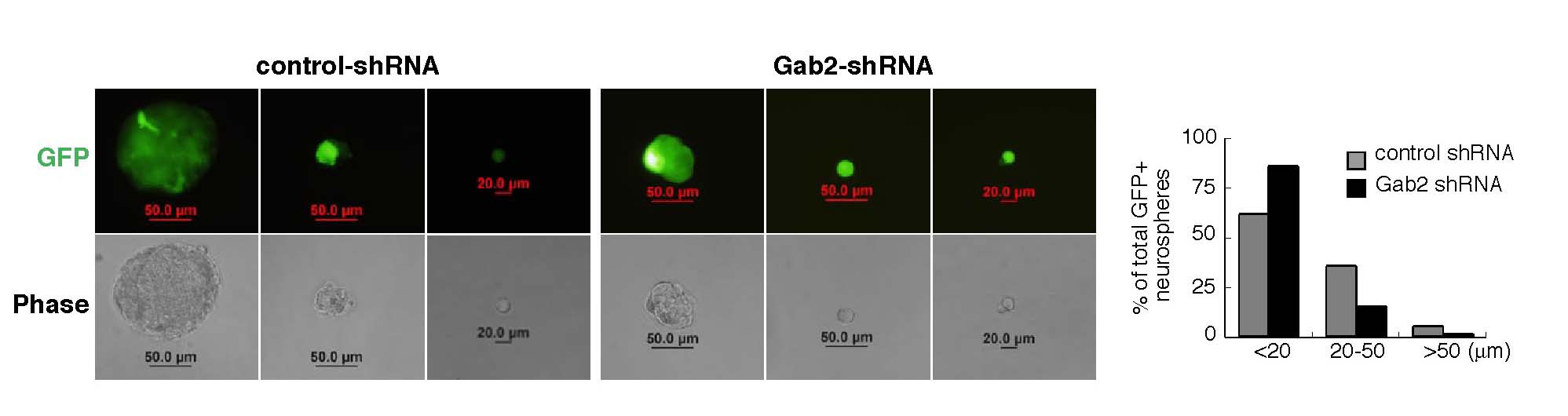
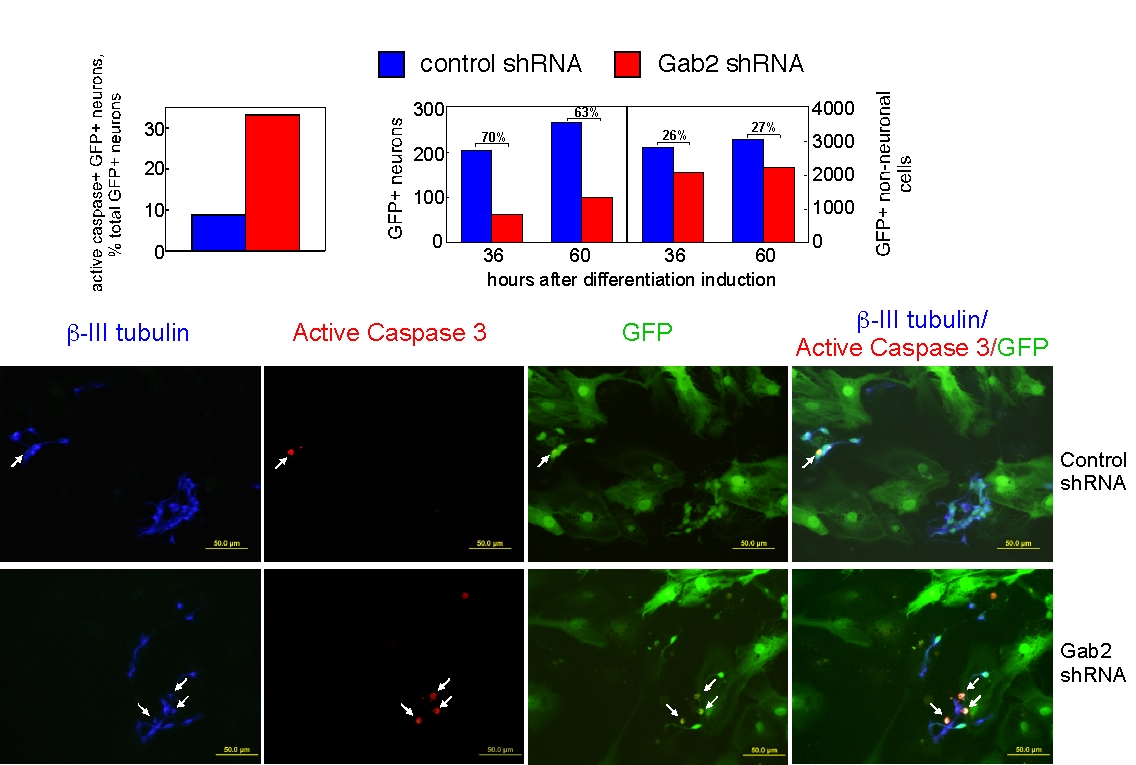
Neural stem cells were transduced with a lentivirus expressing control or Gab2 shRNA. Transduced cells were marked by GFP expression. Cells were dissociated and a clonal assay performed to determine the effect of Gab2 knockdown on bFGF-dependent stem cell proliferation/survival. We found that Gab2 knockdown markedly decreased the ability of bFGF to support stem cell expansion. Neural stem cells were transduced as described above and the effect of Gab2 knockdown was assessed on survival and production of progeny. Our data show that Gab2 provides essential survival signals to neurons since its downregulation greatly increased neuronal apoptosis(identified by staining with an antibody that recognizes active caspase 3) and consequently neuron output.